Monday, August 31, 2015
How to Help Your Kids in a New School?
It is very hard to
get admission in good schools but while kids succeed, parents must prepare their
children into adjusting in new schools. There they are introduced with new
friends, new teachers, new traditions with a fully strange environment. Aside
it, they have a fresh memory of previous school’s friends where they studied
for one or more years, since they have to learn new place’s rules. Transition
from a school to another brings unexpected situations for children as well as
their parents and parents find them in a dilemma of how to tackle the
situations. Here are some practical ways to help your kids in new school’s
environment.
Find someone known. Usually parents want to admit their children in a new but prestigious school
where a child from our friend circle or relations is studying already. If you
know that little child, you may contact him/ her to go with your kids. He/ she
will feel comfortable with a known smiling friend in a new school.
Motivate your children. Children are like blank paper on which you can write
what you want to read. While they are moving from a school to another, you
should prepare them mentally so they can feel relax in new school as if they
are ready to grab the new opportunities. Sometimes it may take time, but it is
much better to make them understand that they are going to a better school.
Welcoming teachers. In a new school, a teacher is the most expected person who can help a
child. You should consult with your kid’s new class teacher to request for the
kid. He/ she would be pleased to help into adjusting in new environment. While
the child will see the known face as a teacher he/ she will feel ease to
express his/ her emotions and will say thanks to parents.
Get your kid’s registration in co-curricular
activities. As a parent you know what
your child’s favorite activity is. Meet school administration to gather details
about co-curricular activities in school. It is another relaxing way to adjust
in new school, so your child can learn to interact with new social groups of
friends. This activity will not only help him/ her in school life but will lead
him/ her to all walks of life.
Teach your kid making new friends Although making new friends is a by-birth
qualification but with little practice you can teach it to you child. Assignment Help Making
new friends will always help your children to find new friends at everywhere
whether he/ she is going to heaven or a war front. Besides it, this will
initiate social characteristics in the child so he/ she can make friends anywhere
regardless the even or odd situations.
Different Leadership Theories
This blog post by the team of assignmenthelpexperts.com would help our students and readers learn about different leadership theories. Leadership can be defined as the process of influencing the behavior of others to work eagerly and passionately for achieving the predetermined goals. Some specific theories of leadership are as follows:
Great Man Theories: This theory is based on the term of military leadership, because at the time, leadership primarily thought about male quality. It is one of the first attempts to explain the leadership. This concept also refers to belief that great leaders are not made but born with unique characteristics (Schyns and Meindl 2005).
Trait Theories: It shows the characteristics and leadership quality of both successful and unsuccessful leader. It is a logical pleasant theory. Trait theory creates awareness among managers about their weaknesses and strengths. Additionally it also helps the leaders to understand quality of a good leader (Winkler 2009). This theory of leadership also explores that some an individual born with some traits but few leadership traits are developed by his efforts. It identifies the intelligence and knowledge level of a manger related to the particular task. It also shows the level of energy and confidence of leader.
Contingency Theories: This theory of leadership is basically focuses on individual variables as per the environment. It suggests leaders that which traits are adopted as per the environment or task. Additionally, in this, style leader always identifies favorable and unfavorable situations (Wart 2007). This also maintains and describes the relationship between leaders and subordinates. Contingency leadership theory explains leadership in term of individual and as well as response of group.
Situational Theories: This theory refers to those leaders, which are flexible for each situation and implements best course of action as per environmental changes. This theory is also known as life cycle leadership theory. The situational leadership theory refers to most effective leadership style the level of maturity (Bryman 2011), for example, Richard Benson, who manages his leadership behavior as per different situations.
Behavioral Theories: This theory is based on the belief that great leaders are not born and they are made. This theory is not assumed the mental quality and internal status of leaders but only focus on the actions of the leaders (Wart 2007).
Participative Theories: This theory is suggested the ideal leadership style that takes the input of subordinates and followers. Formal authority is in hands of leaders but he always takes suggestion and ideas from followers to manage situation as well. In participative theory leaders treats to subordinates as equal and encourage them to work with zeal and enthusiasm (Kusluvan 2003).
Management Theories: This theory is also called as transactional theory. It concretes on the supervision of organization and all managerial activities. Management theory is also based the system of giving punishments and rewards. When the employees are successful, the management gives rewards and vice versa. This theory also emphasizes the procedures and efficiency of organization, and as well as rules and contracts (Schyns and Meindl 2005).
Great Man Theories: This theory is based on the term of military leadership, because at the time, leadership primarily thought about male quality. It is one of the first attempts to explain the leadership. This concept also refers to belief that great leaders are not made but born with unique characteristics (Schyns and Meindl 2005).
Trait Theories: It shows the characteristics and leadership quality of both successful and unsuccessful leader. It is a logical pleasant theory. Trait theory creates awareness among managers about their weaknesses and strengths. Additionally it also helps the leaders to understand quality of a good leader (Winkler 2009). This theory of leadership also explores that some an individual born with some traits but few leadership traits are developed by his efforts. It identifies the intelligence and knowledge level of a manger related to the particular task. It also shows the level of energy and confidence of leader.
Contingency Theories: This theory of leadership is basically focuses on individual variables as per the environment. It suggests leaders that which traits are adopted as per the environment or task. Additionally, in this, style leader always identifies favorable and unfavorable situations (Wart 2007). This also maintains and describes the relationship between leaders and subordinates. Contingency leadership theory explains leadership in term of individual and as well as response of group.
Situational Theories: This theory refers to those leaders, which are flexible for each situation and implements best course of action as per environmental changes. This theory is also known as life cycle leadership theory. The situational leadership theory refers to most effective leadership style the level of maturity (Bryman 2011), for example, Richard Benson, who manages his leadership behavior as per different situations.
Behavioral Theories: This theory is based on the belief that great leaders are not born and they are made. This theory is not assumed the mental quality and internal status of leaders but only focus on the actions of the leaders (Wart 2007).
Participative Theories: This theory is suggested the ideal leadership style that takes the input of subordinates and followers. Formal authority is in hands of leaders but he always takes suggestion and ideas from followers to manage situation as well. In participative theory leaders treats to subordinates as equal and encourage them to work with zeal and enthusiasm (Kusluvan 2003).
Management Theories: This theory is also called as transactional theory. It concretes on the supervision of organization and all managerial activities. Management theory is also based the system of giving punishments and rewards. When the employees are successful, the management gives rewards and vice versa. This theory also emphasizes the procedures and efficiency of organization, and as well as rules and contracts (Schyns and Meindl 2005).
Wednesday, August 26, 2015
Football World Cup Marketing Strategy Paper
In this assignment help you will get the original paper of the below assignment :
Task 2 Six Sigma Essay Brief
You are a Black Belt in an organisation and
your marketing team want to run an advertising campaign based on people sharing
birth dates with footballers. Your boss
thinks that is a bad idea as the company will be giving away a lot of products
based on the quote he found.
“Analysis
of the country squads in the last 6 World Cups finals (1990 -à 2010) shows that out of the 12
squads there are 20 co-incident birth dates.
(A World Cup Squad is 22 – 23 people). Furthermore two of the finals
have provided 5 co-incident birth dates.”
He has asked you to clarify the situation
and has set up a meeting with marketing team for you to present your findings.
When
creating your report be clear about any assumptions and your rationale for
making them. Provide any supporting arguments or
demographics and theories on both sides of your argument.
Consider the
data and how robust it may or may not be or bias that may be present. Try to rationalise the problem using the Six
Sigma RDMAIC methodology including some form of control mechanism.
Instructions
·
The population of the audience
needs to change to an actual area like London or Kent
·
The specific population needs
to be defined (e.g. 10 million)
·
The assumptions made need
regarding the probability rate between the footballers’ birth-rates and the
audience need be more explicitly discussed in the essay and especially for how
they might affect the end results
·
The DMAIC methodological
process used needs to be better discussed for how each of the components relate
to the hypothetical case study
·
The graphs need to be better
discussed in the essay
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Introduction.. 1
The Campaign.. 2
THE DMAIC METHODOLOGY.. 3
Figure 1: The DMAIC Methodology. 3
DEFINE.. 4
MEASURE.. 4
IMPROVE.. 5
MEASURE.. 5
ANALYZE.. 6
CONTROL. 9
Conclusion.. 11
References. 12
Appendices. 13
Appendix 1. 13
1) Birthdays of players of last 6 World Cups with Coincidences. 13
2) No. of players having the same Birthday in each day of the
year 20
Introduction
The
aim of this assignment is to explore the application of Six Sigma on the
marketing operations of a sportswear manufacturing firm. In particular, the case
study focuses on the firms’ marketing option for promoting its products on the
basis of people sharing the same birthdates with footballers. By having access to the birthdates of
footballers involved in the last five world cups, useful information is
obtained that could be utilised for how an overlap between the audience’s
birthrates could generate interest for selling its products. The firm is
considering whether the implementation of such project could be cost effective
depending on the probability of overlap between the birthrates shared by the
audience as well as the footballers. The case study assumes that the firm’s
manager remains uncertain for the actual economics benefits of the marketing
activity. Hence, this report comes to address the reasons for which this
marketing activity could be effective. The report makes use of the Six Sigma
DMAIC methodology in order to justify its argument.
The Campaign
Football remains a popular game which
is played globally and attracts the largest number of audiences. The world cup is celebrated as a global
festival and has the maximum rate of capturing audiences from any part of the
globe. The World Cup took place last time in 2010, in South Africa, and ran
from June 11th to July 11th. The event was well organized
and closed with receiving huge success. The football matches
were played in ten stadiums that were hosted in nine
cities around the country. The final game was played at the Soccer
City stadium
in Johannesburg which is South Africa's
largest city. Details about the 2010 world cup final are shows on Table
1
Table 1: World Cup
Final
Date
|
11th
July
|
Ground
|
Johannesburg FNB Stadium
|
Audience
Capacity
|
84,490
|
No.
of players in the squad for the teams playing finals
|
46
|
No.
of instances of Birthday coincidences
|
2
|
Source:
Taking the 2010world cup final into consideration and
analyzing from the data from the past 5 world cups, the marketing campaign discussed
in this report, is targeting the 2014 world cup final. The initial marketing
plan was to give autographed t-shirts to all those lucky audiences who happen
to share their birthday with any of the members of the 2 teams playing. However,
the plan turned out to be economically unviable. So the marketing team modified
it to include lesser number of people but each getting a larger valued
prize. We will be describing the issue
with the help of the DMAIC Methodology.
THE DMAIC METHODOLOGY
As Figure 1
illustrates and Yang and El-Haik (2009) argue, DMAIC represents a Six Sigma
project methodology. This is a standardized and formal problem solving process
that helps accelerate the rate of efficiency with which decisions are taken but
also implemented in an organization. The acronym DMAIC stands for a standard
set of activities which are to a) Define, b) Measure, c) Analyse, d) Improve
and e) Control processes (Gygi, et al. 2005). Each stage is comprised by the
performance of specific activity/task and this is illustrated on Table 2.
Table
2: The stages of the DMAIC methodology
Define
|
Set the context and objectives for the project
|
Measure
|
Get the baseline performance and capability of the process or system
being improved
|
Analyse
|
Use data and tools to understand the cause-and-effect relationships in
the process or system
|
Improve
|
Develop the modifications that lead to a validated improvement in the
process or system
|
Control
|
Establish plans and procedures to ensure the improvements are
sustained.
|
Source: Gygi, et. al. (2005, p.42)
DEFINE
The problem here is to launch a campaign based on
people sharing birth dates with footballers. The campaign is expected to
attract maximum audience leveraging the viewership of a world cup match
especially the finals. Also the campaign should abide to the cost constraints
the company is ready to fix.
MEASURE
Data for the birthday details for player playing last
5 World Cups are tabulated and attached in Appendix 1.
Initial
Plan
Plan - Give prizes to all spectators with birthdays
coinciding with those of the players playing the finals
No.
of players in the squad for the teams playing finals: 46
No.
of instances of Birthday coincidences: 2
No. of different birth days: 44
No. of spectators for the finals: 84490
Assuming that birthdays of the spectators are evenly
distributed over the 365 days of the year-
No. of spectators having birthdays on a particular day
of the year=
= 231.47 » 232
No. of spectators having birthdays in all the 44 days
= 232 x 44 = 10208
Cost of T Shirt = £10
Total cost incurred = 10 x 10208 = £102080
IMPROVE
The new plan is to implement the above plan with
slight modifications. In this, we plan to offer prizes to those lucky ones
whose birthday falls on the same day as more than one player playing the
finals. Such instances are rarer compared to the instances of the initial plan
and hence offer prizes to lesser number of people while the value of the
campaign remains the same. The measurement of the new plan is shown below.
MEASURE
Modified Plan - Give prizes to all spectators whose
birthday falls on the same day as more than one player playing in finals.
No.
of players in the squad for the teams playing finals: 46
No.
of instances of Birthday coincidences: 3 (Considering average over previous 5
world cup finals)
No. of different birth days: 3
No. of spectators for the finals: 84490
Assuming that birthdays of the spectators are evenly
distributed over the 365 days of the year-
No. of spectators having birthdays on a particular day
of the year=
= 231.47 » 232
No. of spectators having birthdays in all the 3 days =
232 x 3 = 696
Cost of mobile = £50
Total cost incurred = 50 x 696 = £34800
ANALYZE
The
modified plan is so much feasible and implementable. It is also very
cost-effective from the company point-of-view. Implementing such a
comprehensive campaign can reach to a large mass of audiences and can add value
to the company. Moreover, sponsoring prizes on an event like world cup finals
will give enough opportunity to the company to show its products to a larger
mass of audience.
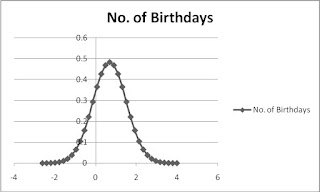
A
normal distribution curve is drawn taking in to consideration the number of
people having the same birthday in a year. For this purpose, the sample of the
253 birthdays of the different players playing in the finals of the world cup
are used.
For
plotting the above distribution curve, the mean and standard deviation of the
number of people in the sample having birthdays on each day of the year are
used.
Mean
= 0.693
Standard
Deviation = 0.824
Form
the data collected, we have also concluded that the maximum number of players
having the same birthday during any day in 4.
The
above graph is a representation of the birthdays of the players distributed
over the 12 months in one year. We can conclude from the above graph that the
birthdays are almost uniformly distributed throughout the 12 months. This graph
is generated using the information provided in the excel sheet. The information
so derived is used to extract the assumption that the birthdays of the
spectators will be evenly distributed throughout the year. The mean number of
birthdays in a particular month comes out to be approximately 23. The
coincidences in the birthdays were also plotted and the graph came out to be as
given.
The
graph shows the numbers of coincidences in a year as well as in a month. In the
first graph we can see that there are coincidences of birthdays of the players
at least once in all the months except March, April and December. An average of
2-3 coincidences occurs in most of the months. It can also be noted that an
average of 3-4 coincidences occur every year. This means that in the world cup
finals matches there is a consistency in the numbers of coincidences over the
years. Both graphs show the pattern between the number of birthdays as well as
the numbers of coincidences. This observation has helped us in deriving the
assumptions for the probability of birthdates for the 2014 world cup.
CONTROL
The
whole campaign needs to be launched before the official start to the world cup.
Efforts should be made to advertise the offer from the company throughout the
world cup matches. The modified plan and its measurement is clearly described
in the above categories which needs to be implemented in the most systematic manner
it can be implemented.
Figure
2: The development of new process through the DMAIC
approach
Conclusion
The aim of this report has been to examine the case of
a marketing strategy that is based on the probability of birthdates which are
shared between footballers and the audience attending the football World Cup in
2014. The report examines whether the marketing strategy could be viable to
employ by using the Six Sigma DMAIC methodology. By looking at the birates
between footballers over the last five world cup finals it can inferred that
2-3 coincidences occur in a month. This report argues that because of the high
number of audiences sharing the same birthday with the footballers the company
needs to change its marketing strategy in order to make it economically viable.
This can be done by offering prizes to individuals whose birthdates happen to
fall on the same year with two footballers. This way the probability is
decreased whilst the company minimises its expenditure and risk on the
marketing strategy.
Breyfogle,
F., Beckimeadows, C. (2001) Managing Six
Sigma. London: John Willey and Sons
Gygi, C., DeCarlo, N., Williams, B. (2005) Six Sigma for Dummies. Hoboken, NJ.:
Wiley Publishing
Salman
Taghizadegan, S. (2006) Essentials of
Lean Six Sigma. Butterworth–Heinemannp
Yang, K., El-Haik, S. B. (2009) Design for Six Sigma. A roadmap for product development (2nd
edition), New York: McGraw Hill